26. Megachile (Pseudomegachile) ericetorum Mitchell, 1927
Megachile ericetorum Female |
Megachile ericetorum Male |
Megachile ericetorum Lepeletier, 1841. Hist. Nat. Insect. Hymen. 2: 341 (♀, ♂).
Megachile cristata Dufour, 1841. Mem. Acad. Sci. Inst. Fr. 7: 420.
Megachile fasciata Smith, 1844. Zoologist 2: 694 (♀).
Megachile rufitarsis Smith, 1844. Zoologist 2: 695 (♂) (preoccupied).
Megachile pyrina Nylander, 1852. Notis. Sällsk. fauna et flora Fenn. Förh. 2: 275 (♀, ♂) (preoccupied).
Megachile senex Smith, 1853. Cat. Hym. Brit. Mus. 1: 160.
Megachile tsingtauensis Strand, 1915. Entomol. Mit. 4: 75.
Chalicodoma (Pseudomegachile) ericetorum euroa Tkalců, 1988. Věst. Českoslov. spol. zool. 52 (1): 49.
Chalicodoma (Pseudomegachile) ericetorum melaleuca van der Zanden, 1989. Entomol.Abh. Staatliches Mus.Tierk. Dresden. 53(6): 72.
Chalicodoma (Pseudomegachile) ericetorum oraniensis van der Zanden, 1989. Entomol. Abh. Staatliches Mus. Tierk. Dresden. 53(6): 72.
Diagnosis.The female of M. ericetorum can be recognized by the combination of 4-dentate mandibles which lack cutting edges, and clypeus with apical edge with a small median tubercle. They are most similar to M. montivaga. Females of M. montivaga lack the median tubercle on the clypeus, and have 5-dentate mandibles. The male of M. ericetorum can be recognized by the combination of combination of simple, yellow front tarsi, 3-dentate mandibles lacking lower process, T5 with a white apical fascia, and T6 without white tomentum above to carina. They are most similar to M. coquilletti. Males of M. coquilletti are typically smaller, and have T6 with the surface above carina with white tomentum dense and conspicuous medially, concealing most of the surface beneath.
FEMALE: Length 14-16 mm.
Head:
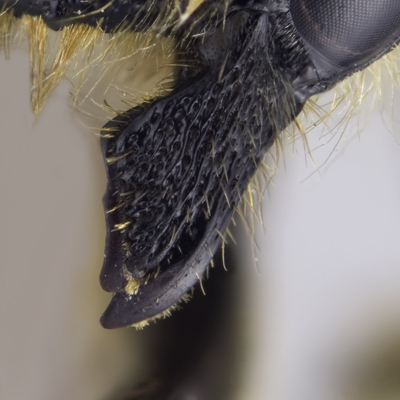
Figure M26: Megachile ericetorum female mandible |
1) compound eyes subparallel to slightly convergent below; lateral ocelli nearer eyes than edge of vertex (3:4), 2) clypeal margin entire, with a small but distinctive median tubercle, 3) mandible distinctly 4-dentate, without a cutting edge (Figure M26), 4) gena slightly broader than compound eye (8:7), 5) punctures fine and close over entire head, shallower but still close on gena, close, almost rugose on frons, supraclypeal area with a distinct median impunctate area in apical half, clypeus with coarser punctures medially, with an small medial impunctate area in basal half, 6) pubescence long and pale yellow on face around antennae and paracoular area, clypeus mosty bare, with a few elongate hairs laterally, sparser and more elongate on gena below, becoming shorter above, with some short, dark, erect hairs intermixed on vertex and along outer edge of upper eye, 7) F1 subequal in length to pedicel and slightly longer than F2, which is quadrate, remaining flagellomeres slightly longer than broad, apical flagellomere longer than broad (3.5:2).
Mesosoma:
1) pubescence yellowish-white, elongate laterally and posteriorly, more elongate on pleura, brownish hairs on mesoscutum medially and scutellum, short and thin, hardly concealing surface, 2) punctures fine and close over most of dorsal surface, pleura finely and closely punctate, propodeum with fine, shallow punctures which are separated by about 1 pd, triangle dull and impunctate, 3) basitarsi shorter and slightly narrower than their tibiae, spurs yellowish, 4) tegula reddish-brown, smooth and sparsely punctate, with short, sparse, pale pubescence in apically, 5) wings hyaline, slightly darker in marginal cell, the veins brown.
Metasoma:
1) narrow and elongate, somewhat parallel-sided, though T1 narrower than T2-T5; T2-T5 rather deeply grooved basally, grooves with a distinct carinate rim, rather deeply depressed apically, T6 rounded to almost truncate in dorsal aspect, almost straight in profile; punctures fine and very close over most of the terga, but becoming slightly more coarse on T5; T1 with elongate yellowish pubescence, T2-T5 with conspicuous entire dense pale yellowish apical fasciae, discal pubescence rather sparse, and entirely yellowish on T2 and T3, with darker hairs apically on T4, and on disc of T5, becoming yellowish laterally, T6 entirely covered with pale yellowish pubescence, becoming rather dense and appressed apically, 2) scopa entirely yellow; S6 rounded, uniformly covered with scopal hairs, with yellowish apical fringe of short hairs, punctures coarse and close, becoming slightly more spaced on apical sterna.
MALE: Length 13-16 mm.
Head:
1) compound eyes very slightly convergent below; lateral ocelli nearer eye than edge of vertex (3:56), 2) clypeal margin slightly produced medially into a small but distinct tubercle, 3) mandible 3-dentate, lacking lower process, 4) gena subequal to compound eye in width, with a concavity at lower angle densely covered with long yellow pubescence, 5) punctures fine and close over most of head, including on clypeus and supraclypeal area, slightly separated laterally on frons, 6) pubescence elongate and copious, white to pale yellow on face below median ocellus and on lower margin of gena, sparse on gena above and on vertex, though vertex usually with some intermixture of short, erect black hairs, which extend to upper hind eye margin and between lateral ocelli, 7) F1 about as broad as long and subequal in length to pedicel, following flagellomeres considerably longer than broad (3:2), the apical flagellomere elongate, about twice as long as broad.
Mesosoma:
1) pubescence entirely white to pale yellow, elongate and dense laterally and posteriorly, becoming shorter and more sparse dorsally, surface visible, front tarsal fringe entirely pale pubescent, 2) punctures fine and close on mesoscutum, scutellum, and pleura, propodeum smooth and more sparsely punctate, triangle somewhat dull and impunctate, 3) front coxal spine short but distinct, rather narrow with a rounded tip, with short, erect, dense reddish pubescence on anterior surface of spine, coxa sparsely pale pubescent, surface shining with sparse but distinct punctures; front basitarsus narrow, pale brownish basally, becoming yellow apically, tarsomeres yellowish, tarsomere 2 with a dark spot ventrally, mid and hind basitarsi dark, slender and relatively long, but shorter than their tibiae, spurs yellowish-brown, 4) tegula brownish, shiny and sparsely punctate, with sparse yellow pubescence uniformly covering surface, 5) wings hyaline, slightly darker in marginally cell, the veins brownish-black.
Metasoma:
1) parallel-sided, T2-T5 with basal depressions with carinate rims, depressed apically, margin impunctate and hyaline, T6 vertical in orientation, disc finely and densely punctate, carinate rim with deep median emargination, this possibly obscured by the irregular, sometimes deep lateral crenulations, apical margin of T6 without teeth, T7 broadly rounded to truncate, with short but distinct apical spine; punctures fine, close and contiguous on T1-T5, with narrow but shining interespaces ≤ 1 pd; pubescence pale yellow, elongate, somewhat sparse on T1, T2, a basally on T3, T4-T6, and apical half of T3 with elongate, black discal pubescence; T3-T5 with entire, whitish apical fasciae, fascia very narrowed medially but entire on T2, 2) S1-S4 exposed, S2-S4 with wide hyaline apical rims, S3 and S4 distinctly emarginate medially; sterna with rather fine and close punctures, S1-S3 with short, sparse pale pubescence on discs, S1-S4 with more dense, elongate pale hairs laterally.
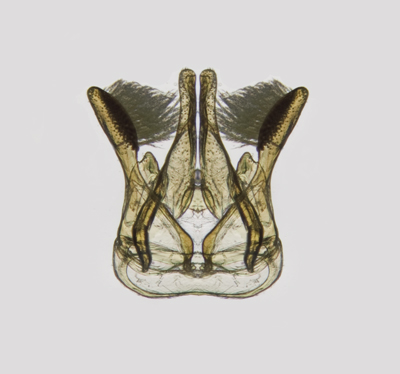
Genitalia: Figure G26.
|
Figure G26: Megachile ericetorum genitalia |
Discussion:
Only recently recorded in the Western Hemisphere (Sheffield et al. 2010), and known from a single female collected in St. Catharines, ON. There is no indication that this species has established in North America. Megachile ericetorum nests in pre-existing cavities, and accepts trap nests (Table 1). A brief account of its biology is presented by Sheffield et al. (2010).
Distribution:
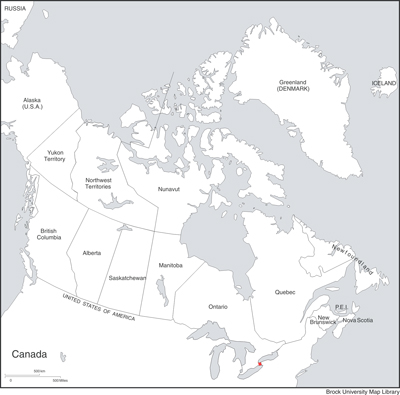
St. Catharines, ON (see Map 26).
|
Map 26: Canadian distribution of Megachile ericetorum |